WebRTC Anonymity and Camouflage Setup: Preventing WebRTC Leaks
Most conventional proxy-changing tools do not fully support protocols that use UDP (including WebRTC, QUIC, and HTTP3). This often leads to the exposure of the original IP address, resulting in WebRTC leaks. This document will guide you through configuring the WifiSocks router proxy to effectively achieve WebRTC anonymity, fix WebRTC leak issues in web browsers, and spoof WebRTC IP addresses.
1. Background Knowledge
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a P2P communication technology between browsers that doesn’t require intermediate software. WebRTC connections use the UDP protocol for data transfer. WebRTC identifies the public IP address via a STUN server.
When using a proxy: For WebRTC to function reliably, the proxy must support the UDP protocol, and the proxy-changing tools must also support UDP. However, current proxy providers often fail to meet this requirement. Even if the proxy supports UDP, the proxy tool might not, leading to the original IP address leak. This significantly compromises anonymity.
The WifiSocks Solution: The WifiSocks team has developed a proprietary solution that allows WebRTC to function effectively and prevent leaks, even when the proxy does not support UDP. This technology not only prevents the exposure of the IP address but can also make the public IP address reported by WebRTC match the proxy’s public IP.
2. Testing Tool
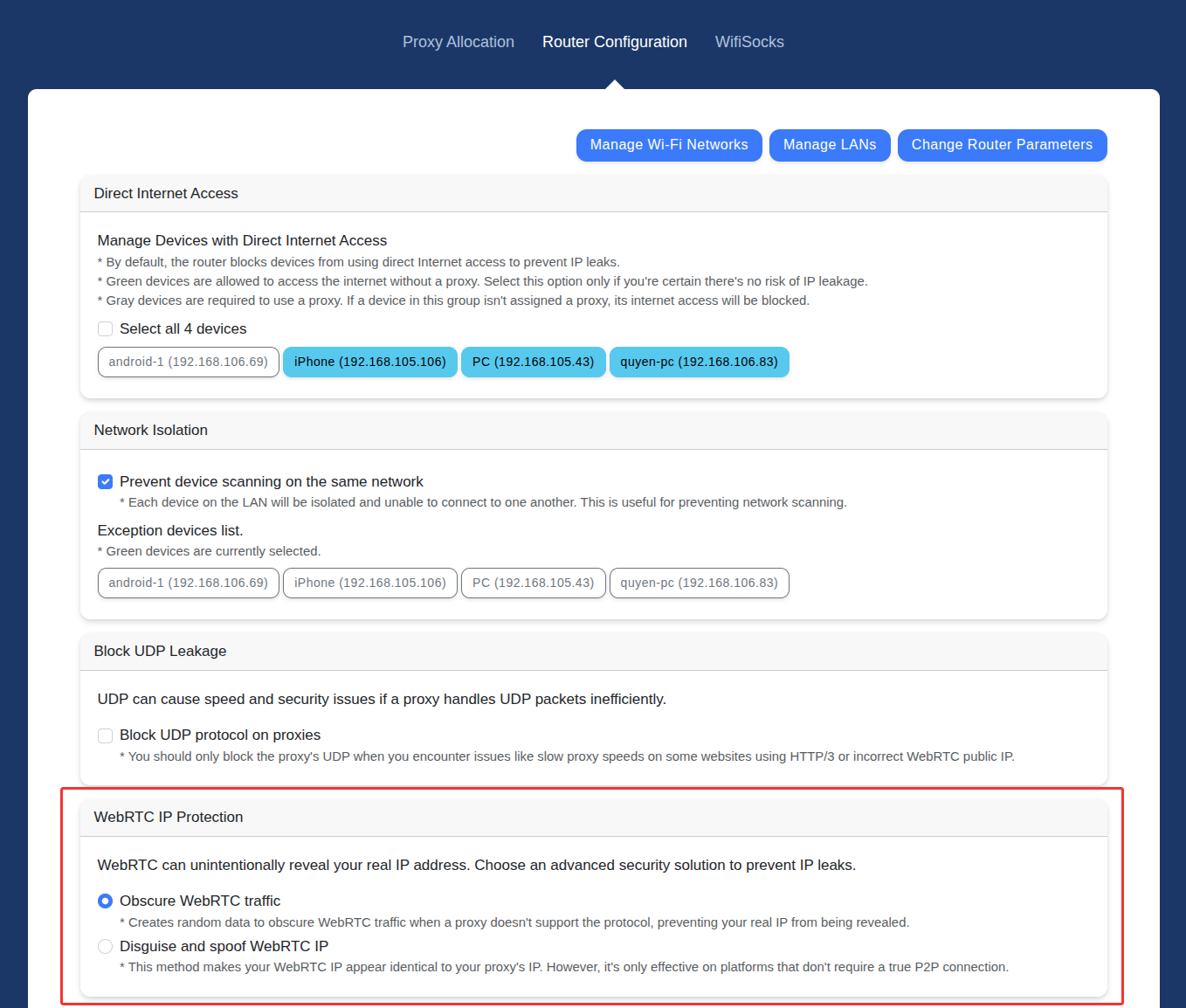
3. Configuring WebRTC on the WifiSocks Router
To protect your privacy, you can configure WebRTC on the WifiSocks router as follows:
- Access the router’s admin interface.
- Navigate to the “WebRTC IP Protection” section under the “Router Configuration” tab.
Here, you have two options:
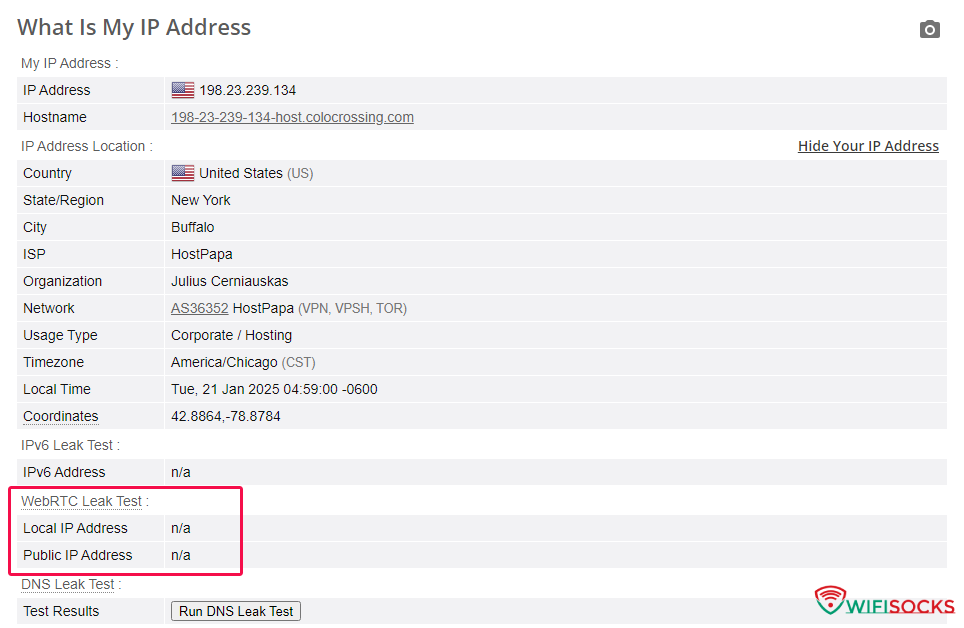
- Obscure WebRTC traffic: This option completely prevents the risk of exposing your real public IP address via WebRTC.
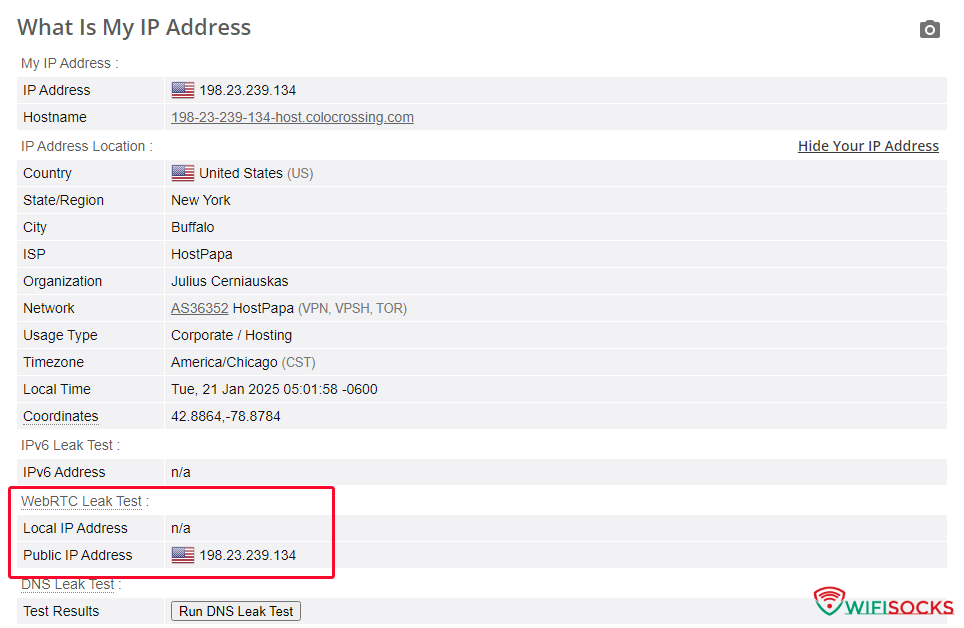
- Disguise and spoof WebRTC IP: In addition to hiding the IP, this option spoofs the WebRTC IP to make it look identical to the proxy’s public IP, even if the proxy does not support UDP.
Choosing the right option:
- If your proxy does NOT support UDP: Depending on your needs, if your only requirement is to block WebRTC packets to prevent the exposure of your original IP, choose “Obscure WebRTC traffic.” If you need to apply the camouflage technique and spoof the WebRTC public IP, choose “Disguise and spoof WebRTC IP.”
- If your proxy supports UDP: You don’t need to worry about this setting; keep the default configuration.
To enhance naturalness and effectiveness, we recommend using a proxy that supports UDP. Blocking or spoofing WebRTC should only be considered as a last resort.
 English
English
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt